The Rubber Manufacturing Process Is a Complex and Fascinating Journey That Transforms Raw Materials Into Indispensable Products Used Across Various Industries. From Tyres to Medical Supplies, Rubber’s Versatility and Durability Make It a Vital Component of Modern Life. This Blog Will Delve Into the Eight Key Stages of the Rubber Manufacturing Process, Exploring Each Step’s Significance, Techniques, and Challenges.
What Is Rubber and Its Importance?
Rubber Is a Unique Elastic Material That Can Be Natural or Synthetic. Natural Rubber Is Derived From the Latex of Rubber Trees (Hevea Brasiliensis), While Synthetic Rubber Is Produced From Petroleum-Based Chemicals. The Importance of Rubber in Various Industries Cannot Be Overstated.
Significance in Industries
- Automotive Industry: Rubber Is Crucial for Manufacturing Tires, Seals, and Gaskets. The Global Tire Market Alone Was Valued at Approximately $250 Billion in 2023, With Rubber Being a Primary Raw Material.
- Healthcare: Rubber Is Used in Medical Devices, Gloves, and Tubing Due to Its Flexibility and Resistance to Chemicals.
- Construction: In Construction, Rubber Is Utilized for Flooring, Roofing, and Insulation Materials.

The Rubber Manufacturing Process Begins With Understanding These Applications, Which Drive Demand and Innovation in the Industry.
Overview of the Global Rubber Market
The Global Rubber Market Was Valued at Around $41 Billion in 2023, With Major Producers Including Thailand, Indonesia, and Vietnam. These Countries Dominate Natural Rubber Production Due to Favorable Climatic Conditions. Synthetic Rubber Production Is Primarily Concentrated in Regions With Strong Petrochemical Industries.
How Are Raw Materials Sourced?
The Sourcing of Raw Materials for Rubber Production Is Fundamental to the Rubber Manufacturing Process.
Types of Raw Materials Used in Rubber Manufacturing
- Natural Rubber: Harvested From Rubber Trees, Natural Rubber Accounts for About 40% of Global Rubber Consumption.
- Synthetic Rubber: Made From Petrochemicals, Synthetic Rubber Constitutes Around 60% of the Market. Common Types Include Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) and Butyl Rubber.
The Harvesting Process
The Harvesting Process for Natural Rubber Involves Tapping Trees to Extract Latex. This Process Includes:
- Tapping: Skilled Workers Make Incisions in the Bark of the Tree to Collect Latex. Each Tree Can Yield Approximately 1 KG of Latex per Day During Peak Seasons.
- Processing Latex: After Collection, Latex Is Processed by Coagulating It With Acids or Salts to Form Sheets or Blocks of Raw Rubber.
Sustainable Sourcing Practices
Sustainability Is Becoming Increasingly Important in Sourcing Raw Materials. Many Manufacturers Are Adopting Practices Such As:
- Certification Programs: Programs Like the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) Ensure That Natural Rubber Is Sourced Sustainably.
- Agroforestry Systems: Integrating Rubber Cultivation With Other Crops Can Enhance Biodiversity and Reduce Environmental Impact.
These Sustainable Practices Are Essential for Ensuring That the Rubber Manufacturing Process Does Not Harm Ecosystems or Local Communities.
What Are the Key Rubber Processing Techniques?
Understanding the Key Techniques Involved in the Rubber Manufacturing Process Is Essential for Producing High-Quality Products.
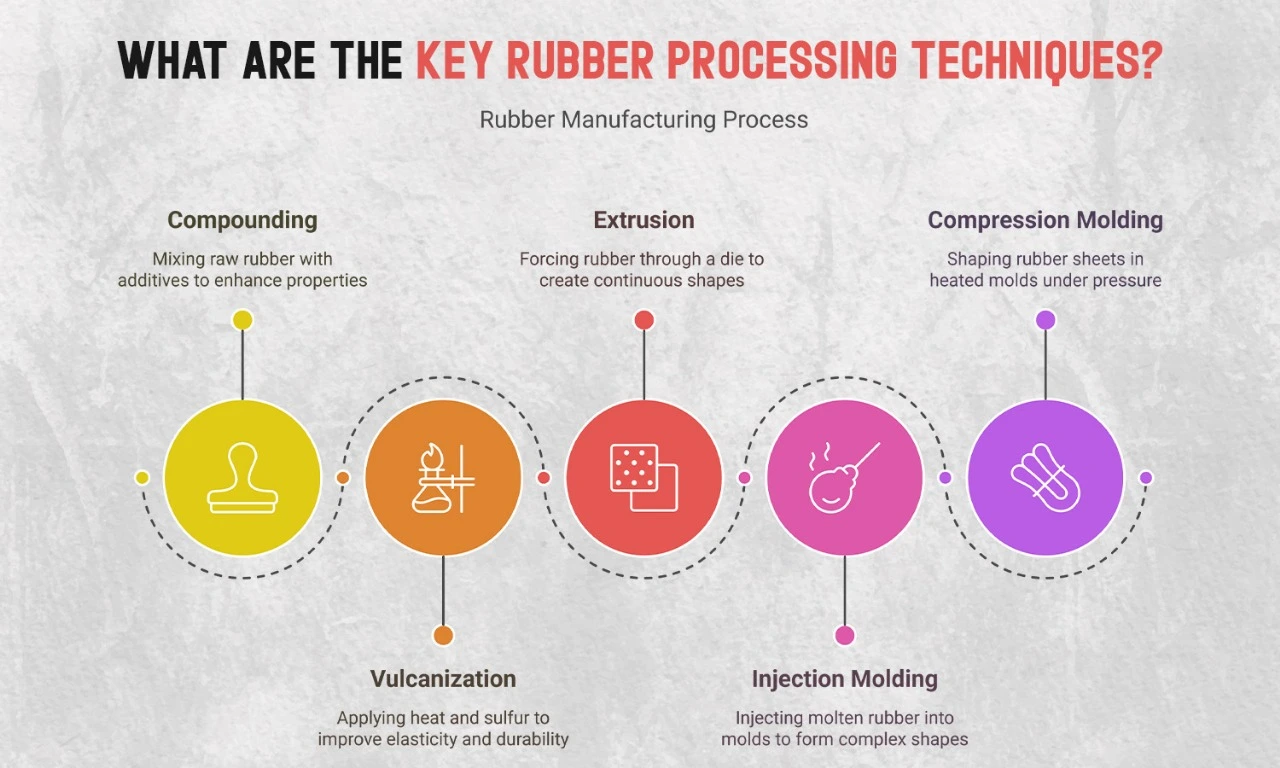
Compounding
Compounding Is a Critical Step Where Raw Rubber Is Mixed With Various Additives to Enhance Its Properties. This Process Typically Involves:
- Additives: Common Ingredients Include Fillers (Like Carbon Black), Accelerators (To Speed Up Vulcanization), Antioxidants (To Prevent Degradation), and Processing Oils (To Improve Workability).
- Mixing Equipment: High-Capacity Mixers Blend These Ingredients Uniformly to Create a Compound That Meets Specific Performance Criteria.
The Compounding Stage Significantly Influences the Final Product’s Characteristics, Such as Strength, Flexibility, and Durability.
Vulcanization
Vulcanization Is a Vital Part of the Rubber Curing Process, Where Heat and Sulfur Are Applied to Improve Elasticity and Durability. This Process Involves:
- Chemical Reaction: When Heated With Sulfur, Cross-Links Form Between Polymer Chains in the Rubber, Resulting in a Stronger Material.
- Temperature Control: Vulcanization Typically Occurs at Temperatures Between 140°C to 180°C for Specific Durations Depending on the Thickness of the Product Being Cured.
This Transformation From Raw Rubber to a Durable End Product Is Crucial for Applications Requiring Resilience Under Stress.
Extrusion and Molding
Shaping Techniques Are Pivotal in Transforming Compounded Rubber Into Final Products:
- Extrusion: In This Process, Rubber Is Forced Through a Die to Create Continuous Shapes Like Hoses or Seals. The Extruded Material Can Then Be Cut Into Desired Lengths.
- Molding Techniques:
- Injection Molding: Molten Rubber Is Injected Into Molds Under Pressure, Allowing for Complex Shapes.
- Compression Molding: Rubber Sheets Are Placed in Heated Molds Where Pressure Shapes Them Into Final Products.
These Shaping Methods Are Essential Components of the Overall Rubber Manufacturing Process, Ensuring That Products Meet Design Specifications.
How Is Quality Control in Rubber Maintained?
Quality Control Is Paramount Throughout the Rubber Manufacturing Process, Ensuring That Products Meet Industry Standards.
Importance of Quality Assurance
Maintaining High Quality Standards Helps Ensure Customer Satisfaction and Safety. Quality Assurance Practices Include:
- Regular Audits of Manufacturing Processes.
- Training Staff on Quality Management Systems.
Testing Methods for Rubber Products
Various Testing Methods Are Employed to Assess Product Quality:
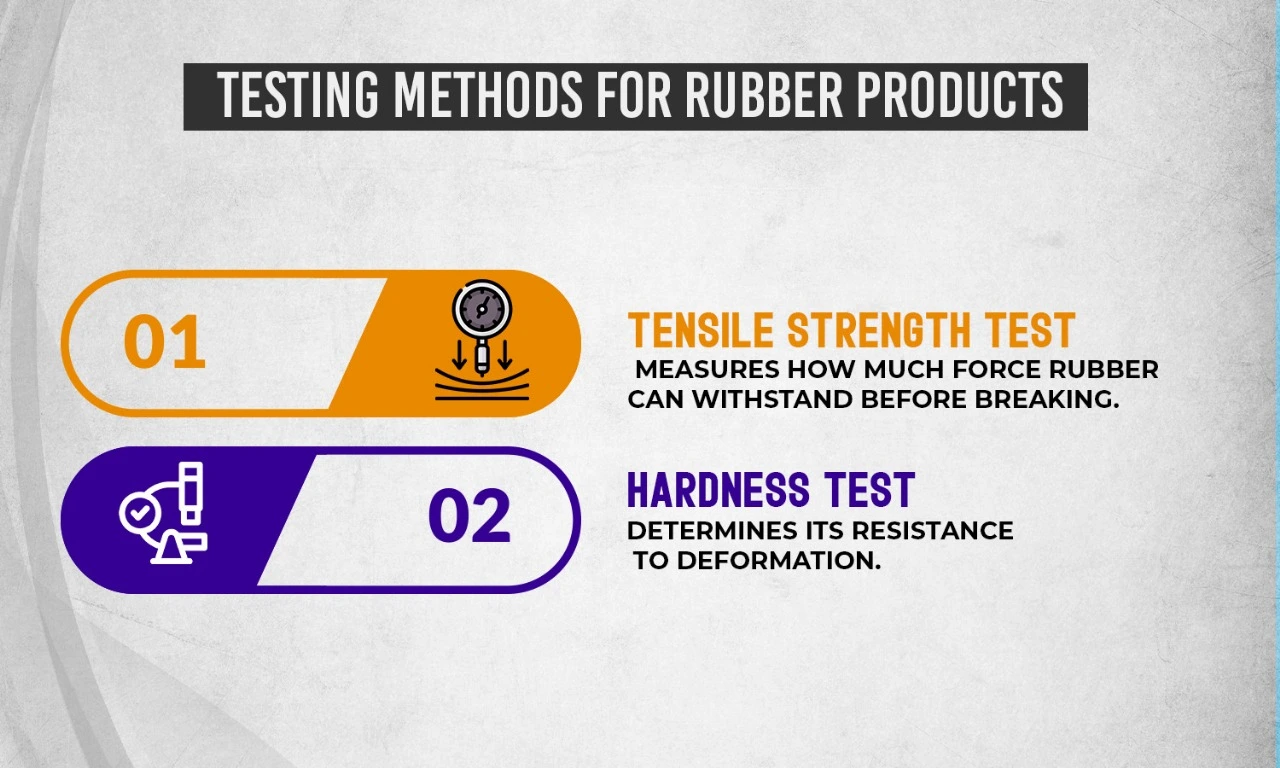
- Tensile Strength Tests: Measure How Much Force a Material Can Withstand Before Breaking.
- Hardness Tests: Determine How Resistant a Material Is to Deformation.
These Tests Provide Critical Feedback on Whether Products Meet Required Specifications Before Reaching Consumers.
Standards and Certifications
Compliance With Industry Standards Such as ISO Ensures Consistent Quality Across All Manufactured Products. Certifications May Also Include:
- ISO 9001 for Quality Management Systems.
- ISO 14001 for Environmental Management Systems.
Adhering to These Standards Helps Manufacturers Maintain Credibility and Trust Within Their Respective Markets.
What Machinery and Equipment Are Used in Rubber Manufacturing?
The Efficiency of the Rubber Manufacturing Processes Relies Heavily on Advanced Machinery Designed for Specific Tasks.
Overview of Essential Machinery
Key Equipment Used in the Manufacturing Process Includes:
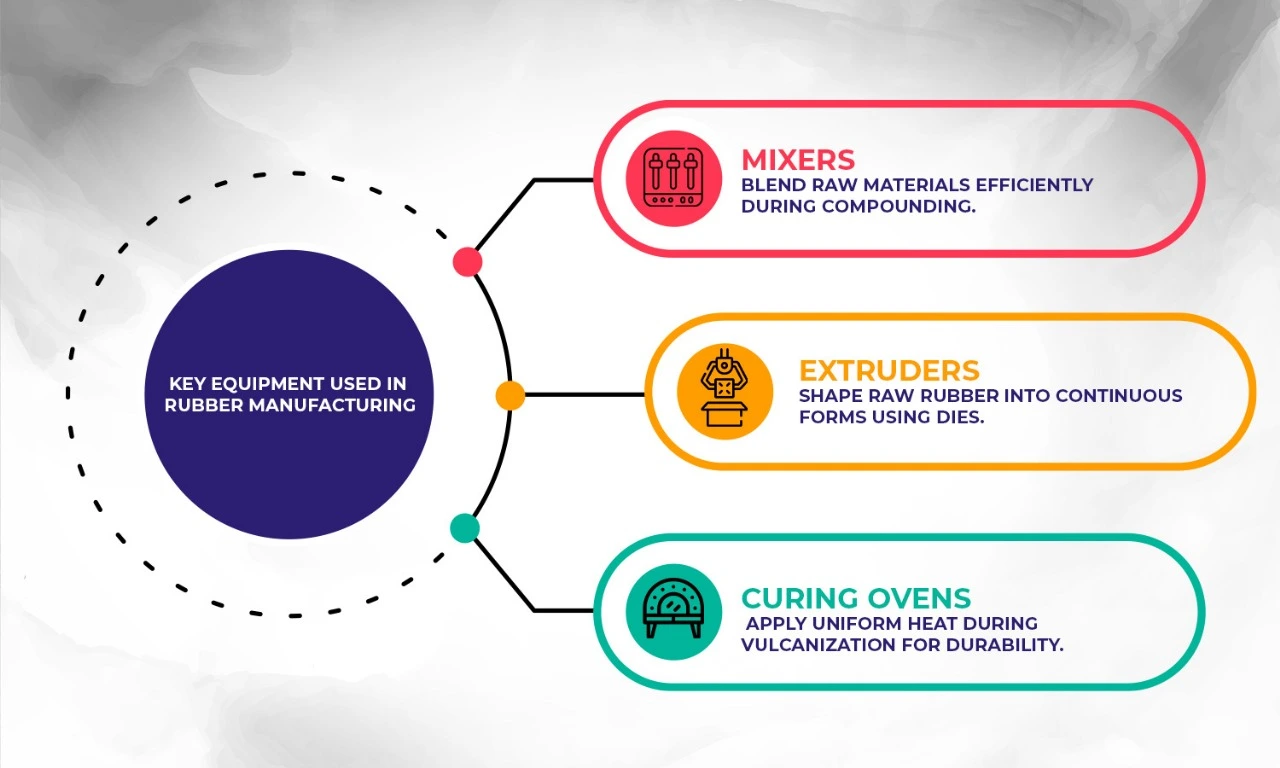
- Mixers: High-Capacity Mixers Blend Raw Materials Efficiently During Compounding.
- Extruders: Machines That Shape Raw Rubber Into Continuous Forms Through Dies.
- Curing Ovens: Used During Vulcanization to Apply Heat Uniformly Across Products.
Each Piece of Machinery Plays a Vital Role in Ensuring Smooth Operations Throughout Production.
Innovations in Machinery
Recent Advancements Have Led to More Efficient Machines That Enhance Output While Reducing Energy Consumption:
- Automated Mixing Systems Improve Consistency in Compounding.
- Advanced Curing Ovens Allow for Precise Temperature Control During Vulcanization.
These Innovations Contribute Significantly to Optimizing the Overall Efficiency of the Rubber Manufacturing Process.
Maintenance Practices
Regular Maintenance of Rubber Processing Machinery Is Crucial for Optimal Performance:
- Scheduled Inspections Help Identify Potential Issues Before They Lead To Breakdowns.
- Implementing Preventive Maintenance Strategies Can Extend Machinery Lifespan Significantly.
Such Practices Ensure That Production Remains Uninterrupted and Efficient Over Time.
What Challenges Are Faced in Rubber Manufacturing?
Manufacturers Encounter Several Challenges That Can Impact Production Efficiency Within the Context of the Rubber Manufacturing Process.
Common Challenges
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Natural Disasters or Geopolitical Issues Can Affect Latex Supply Chains Significantly.
- Fluctuating Material Costs: Prices for Both Natural and Synthetic Rubbers Can Vary Widely Based on Market Conditions and Availability.
Variability in Raw Material Quality
Inconsistent Quality of Raw Materials Can Lead To Production Difficulties:
- Variations in Latex Quality Can Affect Compounding Results.
- Synthetic Rubbers May Have Inconsistencies Due to Variations in Petroleum Feedstocks Used During Production.
Implementing Stringent Quality Checks at Every Stage Helps Mitigate These Risks Effectively.
Strategies for Overcoming Challenges
To Navigate These Challenges Successfully, Manufacturers May Adopt Several Strategies:
- Diversifying Suppliers Can Reduce Dependency on Any Single Source.
- Investing in Technology Can Streamline Processes and Enhance Resilience Against Disruptions.
By Proactively Addressing These Challenges, Manufacturers Can Maintain Steady Production Levels Despite External Pressures.
What Are the Environmental Considerations?
Environmental Sustainability Plays an Increasingly Important Role Within the Context of the Rubber Manufacturing Process.
Analyzing Environmental Impact
The Production of Rubber Has Significant Environmental Implications:
- Deforestation Associated With Natural Rubber Plantations Can Lead To Habitat Loss.
- Chemical Runoff From Manufacturing Processes May Pollute Local Water Sources if Not Managed Properly.
Understanding These Impacts Is Crucial for Responsible Manufacturing Practices That Prioritize Ecological Health Alongside Economic Growth.
Sustainable Practices
Implementing Effective Recycling Methods Can Significantly Reduce Waste Generated During Production:
- Recycling Scrap Rubber Into New Products Minimizes Environmental Footprints While Conserving Resources.
- Utilizing Eco-Friendly Additives Reduces Reliance on Harmful Chemicals During Compounding Processes.
These Sustainable Practices Are Essential Components of Modern Manufacturing Strategies Aimed At Reducing Environmental Impact Throughout the Entire Rubber Manufacturing Process.
Role of Certifications
Certifications Like FSC Promote Sustainable Sourcing Practices That Benefit Both Manufacturers and Ecosystems:
- Ensuring That Natural Resources Are Harvested Responsibly Helps Maintain Biodiversity.
- Compliance With Environmental Standards Bolsters Corporate Responsibility Initiatives Within Companies Engaged in Rubber Production Activities Globally.
What Future Trends Are Emerging in Rubber Manufacturing?
The Future of Rubber Manufacturing Looks Promising With Several Emerging Trends Poised to Reshape Industry Landscapes Significantly Over Time:

Innovations in Rubber Technology
Advancements Include Developing Bio-Based Materials That Reduce Reliance on Fossil Fuels While Enhancing Product Sustainability:
- Bio-Based Rubbers Derived From Renewable Resources Offer Alternatives Without Compromising Performance Characteristics Compared to Traditional Options.
- Research Into New Formulations Continues Evolving Rapidly as Consumer Demand Shifts Toward Greener Solutions Across Various Sectors, Utilizing These Materials Extensively Today!
Impact of Automation
Automation Will Revolutionize Many Aspects Related Directly Back Down Through Each Stage Involved Within This Comprehensive Overview Detailing How Everything Ties Together Seamlessly Throughout All Phases Involved Here Today!
- Enhanced Automation Improves Efficiency While Reducing Labor Costs Significantly Across Multiple Areas Tied Closely Together Throughout the Entire Operations!
- Smart Factories Equipped With Iot Devices Monitor Real-Time Data Analytics, Provide Insights Necessary to Optimize Workflows, and Continuously Improve Productivity Levels Beyond Expectations Set by Previously Established Benchmarks!
Predictions for Future Production
Market Trends Indicate Growing Demand for Eco-Friendly Products, Pushing Manufacturers to Adapt Processes Accordingly to Meet Changing Consumer Preferences Effectively!
- Increased Focus On Sustainability Drives Innovation, Leading Towards More Environmentally Friendly Alternatives Available in the Marketplace Soon!
- Collaboration Between Stakeholders Ensures Alignment, Goals, a Shared Vision Future Success Achieved Collectively Rather Than Individually Pursuing Separate Paths Forward Alone!
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the Complete Journey Involved Within Each Phase Outlined Here Helps Appreciate the Complexities Inherent Within This Intricate System!
- Sustainable Sourcing Practices Are Critical to Minimizing Negative Impacts Associated Directly Back Down Through the Entire Supply Chain Network Established Over the Years Past!
- Key Processing Techniques Such as Compounding, Vulcanization Extrusion Molding Are Essential for Producing High-Quality Results Desired by Customers Worldwide!
- Quality Control Measures Implemented Throughout Ensure Compliance With Industry Standards Is Maintained Consistently Across the Board!
- Advanced Machinery Plays a Vital Role in Enhancing Overall Efficiency, Optimizing Productivity Levels Achieved Consistently Over Time!
- Manufacturers Must Navigate Various Challenges While Adopting Strategies to Overcome Them Effectively, Ensuring That Smooth Operations Are Maintained Uninterrupted!
- Environmental Considerations Are Increasingly Shaping Production Practices, Driving Innovation Towards Greener Solutions Available Marketplace Today!
- Future Trends Indicate a Shift Towards More Sustainable Practices Within Industry, Aligning Goals, Shared Vision, Success Achieved Collectively, Moving Forward Together Collaboratively!
In Conclusion, Dee Pee Rubber Exemplifies Excellence by Understanding and Implementing Effective Strategies Throughout an Entire Comprehensive Overview Detailing How Everything Ties Together Seamlessly Throughout All Phases Involved Here Today! With Commitment, Quality Sustainability Dee Pee Continues to Meet Diverse Customer Needs, Positively Impacting the Environment Simultaneously Ensuring Long-Term Success Achieved Collectively Moving Forward Together Collaboratively!








